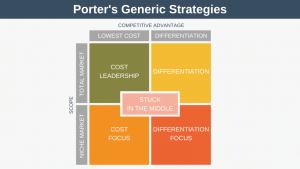
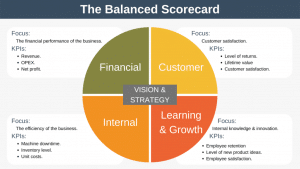
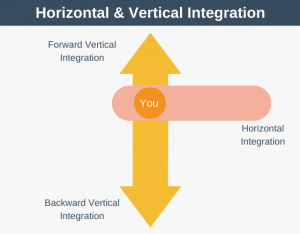
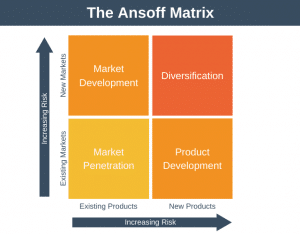
The CAGE Distance Framework is a model that can take some of the guesswork out of deciding which country to target for international expansion.
By using the CAGE Distance Framework, you will understand which markets are straightforward for you to enter and which might be more challenging.
As your company grows, you may decide to expand internationally. Success in implementing an international expansion strategy starts with selecting the right country to enter.
The first step in this process is usually to identify those markets with the greatest sales potential. However, alongside sales potential, a key question to answer is how difficult will it be to grow your business in that country.
The CAGE Distance Framework
Pankaj Ghemawat, a professor of management and strategy at New York University, created the CAGE Distance Framework to answer this question.
The origins of the framework came about when Ghemawat noticed something peculiar – that profit margins tend to be correlated with proximity to a company’s headquarters. For example, Walmarts’s largest profit margins are in Mexico and Canada, and its worst margins are in Germany and China.
From this observation, Ghemawat created the CAGE Distance Framework. CAGE stands for Cultural, Administrative, Geographic, and Economic.
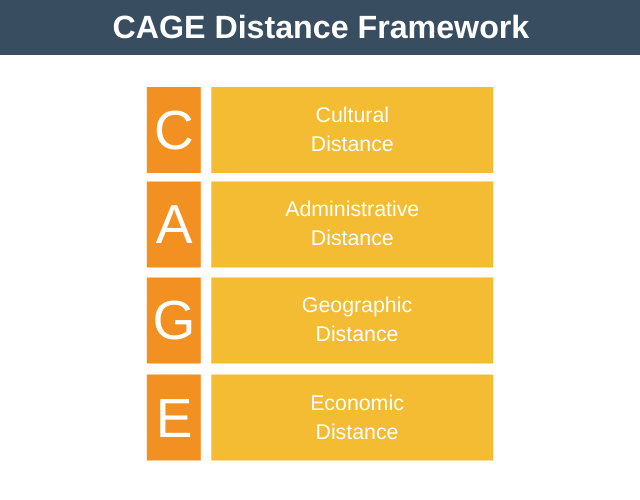
By examining all four categories you’ll get a much better understanding of the “distance” between two countries than just the miles between them.
Ultimately, the CAGE Distance Framework can help you understand the risks of international expansion. Based on this, you can decide whether to:
- Launch or not launch in that country.
- Make changes to your products or services.
- Make changes to your pricing models.
- Make changes to your organizational structure.
There are two parts to performing a CAGE analysis.
- Industry analysis: where you look at which factors your industry is most sensitive to, that is, what factors matter to you.
- Country-level analysis: where you determine which countries are closest to you for the factors that matter to you.
Note
One key feature of the CAGE Distance Framework is that it takes into account both bilateral and unilateral factors:
- Bilateral factors are differences specific to your business and your home market, such as having different languages.
- Unilateral factors apply to the country you’re considering regardless of your home market, for example, a country generally being insular and unwelcoming to foreigners.
Let’s take a closer look at each of the four categories:
1. Cultural Distance
Cultural differences are the differences in beliefs, behaviors, language, values, and norms between two countries.
Typical cultural differences to consider include:
- Different languages or dialects.
- Different ethnicities.
- Other belief systems and religions.
- Different attitudes towards issues.
- Different trust levels.
- Are people culturally insular or open?
- Are people traditional or modern?
Industries impacted by cultural distance include:
- Products that have high language content, such as websites and movies.
- Food industry: certain religions don’t eat certain foods.
- Car industry: people may believe bigger or smaller cars are better.
2. Administrative Distance
Administrative differences are the political and legal differences between the two countries. Administrative differences to consider include:
- Lack of common currency.
- Lack of a shared trading block.
- Different legal system.
- Political hostility to foreign firms.
- Home product bias vs. foreign product bias.
- Presence of corruption.
- Societal conflict.
- Risk of expropriation by the state.
Industries impacted by administrative distance include:
- Producers of staple goods, for example, electricity.
- Drug companies.
- Farming.
- Aerospace.
- Sectors that are vital to national security, for example, telecommunications.
- Natural resource companies.
- Companies with high sunk costs.
3. Geographic Distance
Geographic distance is the physical distance between the two countries. Geographic distance is comprised of more than just how many miles separate two countries and include:
- Physical distance.
- Lack of a shared border, meaning goods must be transported through a 3rd country.
- Size of country.
- Distance between cities.
- Transportation links.
- Differences in climate.
Industries impacted by geographic distance include:
- Low value-to-weight products. For example, bricks are expensive to transport large distances, especially considering their low cost.
- Fragile products.
- Perishable products.
- Service businesses.
4. Economic Distance
Economic distance is the financial distance between two countries’ wealth, income, and labor costs. Economic factors to consider include:
- Wealth differences.
- Cost/quality of natural resources. For example, if you make organic smoothies but it’s difficult to get hold of organic ingredients in your target country then that’s a big barrier.
- Infrastructure.
- Knowledge differences.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) differences.
Industries impacted by economic distance include:
- Products where demand changes with income, for example, luxury cars.
- Industries where cost differences are important, for example, clothes.
CAGE Distance Framework Example
For this example, imagine you have a game app that you currently sell in your home market, the US. You want to expand internationally.
You know the biggest market globally by population is China, so you want to investigate launching there. The other country you’re considering is Canada simply because it’s in such proximity to your home market.
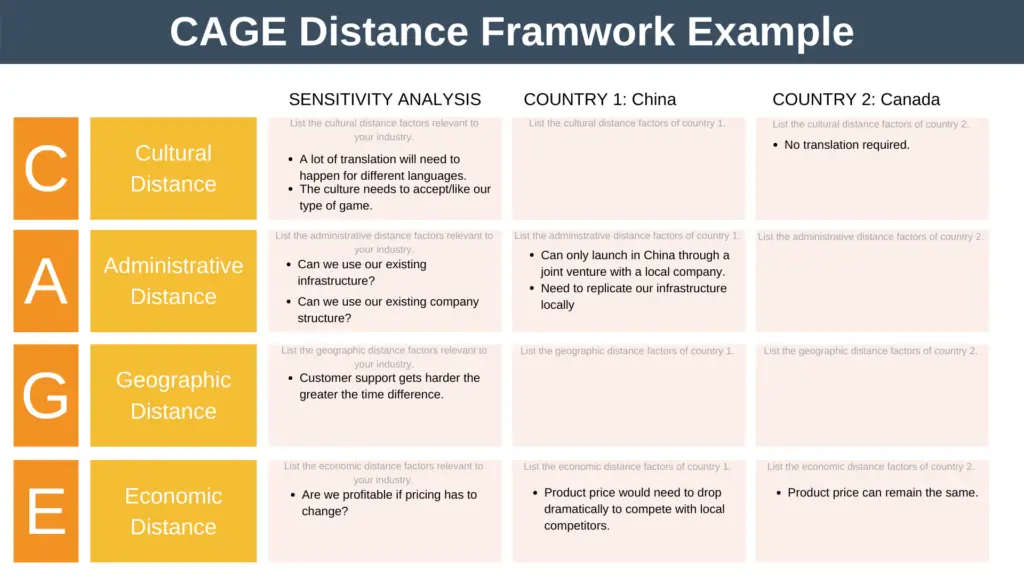
Let’s begin by looking at some of the CAGE factors that are most relevant to your industry:
- Translation will need to happen if languages are different.
- Does the culture like the type of game you’re offering?
- Can you use your existing infrastructure?
- Can you use your existing company structure?
- Can you use current customer support?
- Can you use the current pricing structure?
As you can see from the image, some significant differences exist when we’re investigating launching in China, namely:
- Legally, the product can only be launched in China via a joint venture (JV) with a local company.
- Legally, all infrastructure would need to be hosted in China.
- Your product price would need to drop dramatically to compete against local competitors.
As you can also see, although the profit potential might not be anywhere near as large, there are far fewer barriers to launching in Canada.
Once you’ve completed your CAGE Distance Framework analysis, it’s then up to you to balance risk against reward and decide which territory makes the most sense for you to enter.
CAGE Distance Framework Template
If you’d like to conduct your own analysis using the model, you can download out CAGE Distance Framework Templace here.
Advantages and Disadvantages
There are several advantages and disadvantages associated with the model.
Advantages
The advantages of the model include:
- The impacts of CAGE distances have been shown quantitatively using gravity trade models. Gravity trade models identify factors that pull economies closer together.
- The model considers bilateral and unilateral distance factors.
- It enables you to identify factors that might handicap you relative to local competitors.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the model include:
- The model focuses on barriers to international expansion but doesn’t help you determine the size of the opportunity.
- You will have to do a lot of research to gain an accurate picture of the country you wish to enter.
Summary
Success in implementing an international expansion strategy starts with selecting the right country to enter.
The CAGE Distance Framework is a model that can take some of the guesswork out of deciding which country to expand into. It helps you to understand the frictions that exist between your home country and the country you’re considering expanding into.