PEST Analysis is a tool that helps you to understand the macro-environment in which an organization functions.
Suppose a company is considering two options:
- Should it develop a new product?
- Or should it expand into a new country?
How would a company decide which opportunity is the right one to follow? Where would you start in answering this question? What are the key pieces of information you would need to enable you to make this kind of strategic decision?
In this article, we’ll examine how a PEST Analysis can be a useful tool in answering these big strategic questions.
PEST Analysis is an acronym standing for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological. It provides a view of the different macroeconomic issues that might affect an organization. The idea is that by understanding what’s changing in the world around you, you will be able to make better strategic decisions.
This is sometimes known as environmental scanning and is an input to setting strategy.
Why Use a PEST Analysis
There are a number of very specific ways in which you can use the tool. It can help you:
- Spot potential opportunities.
- Spot potential threats.
- Understand how the business environment is changing.
- Avoid undertaking projects that go against the prevailing macroeconomic winds.
- Develop business practices that work in alignment with local ways of doing things. This is particularly important if you plan to operate or launch in a new country.
- Question your existing assumptions.
PEST Analysis in Context
A companies environment consists of three levels. These are:
- Internal environment.
- Micro-environment.
- Macroenvironment.
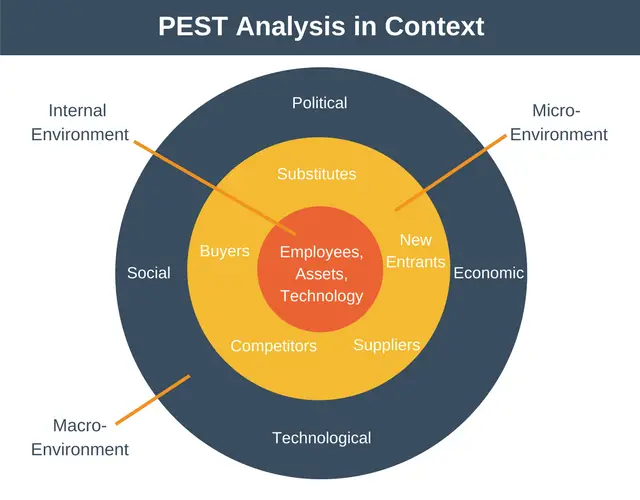
The internal environment consists of factors that are internal to the organization. These factors include employees, assets, and technology systems, etc.
The next level is the micro-environment. These factors are outside the company, but they are still very closely related to the organization. These are the factors that make up the industry the organization operates in. These factors include suppliers, buyers, competitors, and subcontractors.
The final level is the macroenvironment. These are the factors that can influence the organization but the organization itself has no control over. These factors are political, economic, social, and technological. These are the factors a PEST Analysis examines.
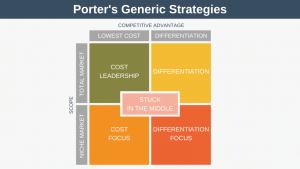
PEST, Porter, and SWOT
PEST Analysis scans the external environment. Conversely, a SWOT analysis focusses internally. It examines the internal aspects of an organization such as strengths as weaknesses.
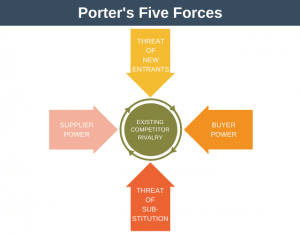
Porter’s five forces can be used to examine the micro-environment. The model looks at factors such as customers, suppliers, and competitors.
Because of this, it is common to use all three tools together.
- SWOT analysis: To ensure that your strategy is the right fit for you.
- Porter’s Five Forces: To understand your immediate business environment.
- PEST Analysis: To ensure the prevailing winds are on your side.
Obviously, the subject of this article is the PEST Analysis, so let’s jump in and take a look.
PEST Analysis
The aim of a PEST Analysis is to collect information about macroeconomic factors to gain insight. This insight can then be used to make better decisions.
Let’s examine each factor of the PEST Analysis in turn. Note that there are many factors you can consider in your PEST Analysis. The real key to conducting a successful PEST Analysis is to understand which are the most important factors for you and your organization.
1. Political Factors
Politics and the action of government has a huge impact on how businesses conduct themselves. It also determines how favorable a country is to do business within. This part of a PEST Analysis is about understanding how shifts in political power structures might impact your business.
For example, consider a country where the government introduces a new piece of legislation. This legislation states that all companies must be carbon neutral within seven years. For some businesses, this may result in an increased cost of launching in that country. For other businesses, it might provide a huge opportunity.
2. Economic Factors
The economic factors part of a PEST Analysis concerns understanding the economic prospects for a country. Here you’ll want to understand, amongst other things:
- Shifting demographics.
- Fiscal policy.
- Market demand.
- Interest rates.
- Infrastructure improvement rate.
Using this information you can then determine if it makes sense to operate within this country or region.
For example, the economy of China has grown massively over the past two decades. This is evidenced by high GDP growth almost every year. This GDP growth combines with a huge internal market of well over one billion people. These factors present a huge opportunity for firms looking to grow. This is especially the case because many western markets are saturated.
3. Social Factors
Social factors include all factors that are social or cultural within a particular country or society. These factors can be some of the most difficult to predict and interpret. These factors include such things as:
- Career expectations.
- Lifestyle preferences.
- Education levels.
- Attitudes.
- Entrepreneurial spirit.
In some countries, for example, it is considered rude to challenge a decision your boss has made. In other cultures, it is actively welcomed.
In France, it is still common practice for employees to take a 2-hour lunch break. In China, office workers expect to receive a promotion every year. To be successful, businesses need to understand these social and cultural nuances.
4. Technological Factors
Technological factors mean macroeconomic technology shifts. Rapid technological change has impacted many businesses since the industrial revolution. Technological factors can influence how you deliver your product or service to the market.
Technological factors can affect both consumers and the company itself. For example, does increased smartphone and broadband penetration offer new opportunities for products? Or does increased automation make a previously uneconomic market accessible?
Technological change is vital to staying competitive. From the industrial revolution to the present day it has been a driving force behind globalization.
How to Use a PEST Analysis
The basic process to perform a PEST Analysis is as follows:
- Determine the most important PEST factors to collect.
- Collect the information.
- Brainstorm Opportunities and Threats.
- Take Action.
Let’s dig into the detail of each step…
1. Determine the most important PEST factors to collect
There is an almost infinite number of factors that you could collect to perform your PEST Analysis. The key to a successful PEST Analysis is to begin by determining which are the most important factors for your organization.
Here is a list of questions to help you get started.
a. Political Factors:
Some of the political factors you should consider in your PEST Analysis are:
- How stable is the political environment? Will a change of government change the business environment?
- How well developed is the rule of law?
- How enforceable is contract law?
- Is there adequate intellectual property protection?
- Is property law adequate?
- Are there likely to be changes to the minimum wage and working time directives?
- What changes are happing to industrial safety regulations?
- Might the government’s approach to any of the following change and affect you:
- Tax law.
- Competition law.
- Corporate social responsibility.
- Environmental policy.
- Can you brainstorm any other political factors that could be subject to change? How might these changes impact you?
As you can see there are many political factors that can influence, for better or worse, your ability to do business within a particular country.
b. Economic Factors
Some of the economic factors you should consider in your PEST Analysis are:
- Is the economy stagnant, growing, or shrinking?
- Is the economy subject to wild fluctuations?
- How stable is the country’s currency?
- Is the government likely to intervene in the market?
- Will it be easy to hire the right labor?
- How high is the employment rate?
- What proportion of labor is skilled?
- What are current labor costs and how is this expected to change?
- How easy is it for businesses or consumers to access credit, and how does this impact your organization?
- What are the long-term prospects for GDP per-capita?
c. Social Factors
Some of the social factors you should consider in your PEST Analysis are:
- What is the local attitude towards foreign products or services?
- Does the population have a strong opinion on environmental issues?
- Are the typical roles of men and women different?
- What is the population’s level of education and health? In what ways are these factors likely to change over time?
- Are there any social attitudes that could affect what you sell or how your business operates?
- How will cultural working arrangements or attitudes to work affect your business? How are these attitudes changing?
- Are there any generational attitude shifts happening?
- Is there a class structure in place and how might this impact your business?
- What leisure interests does the population participate in? Does this present an opportunity or problem for your business?
d. Technological Factors
Some of the technological factors you should consider in your PEST Analysis are:
- Are there any technologies that your business should be using to create products or to deliver products?
- How might new technology impact your product offering?
- How might new technology impact the cost structure of your business?
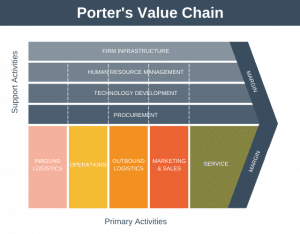
- Might new technology impact your value chain?
- In what industries does this nation have a competitive advantage? How does this impact your business?
- Do technological hubs exist within the country? Can you use one of these hubs to your benefit?
2. Collect the information
Step 1 of performing a PEST Analysis involves determining the factors that are important to your business. You focus only on those factors that you think will help you make better strategic decisions.
Once you have determined the factors you want the next step is to agree who is going to be responsible for collecting each factor, and by when.
3. Analyze the Data
Once you have collected your data you should have good insight into the major trends that are taking place. It is now time to analyze your data to see how it impacts your organization.
This step commonly takes the form of a brainstorming session. In this session you’ll look for:
- Opportunities: What trends can you see in the data that could provide an opportunity for your business?
- Threats: What trends can you see in the data that have the potential to undermine your business?
You may find it useful to weigh each of the factors according to how important it is to your business. This will highlight the most important factors, helping you make better decisions.
4. Take Action
Once you’ve completed your PEST Analysis you rarely immediately take action on your findings. This is because a PEST Analysis is just an input to the strategy process. Many other factors need to be considered before deciding your strategy.
But what you will want to do is determine what are the next steps in your strategic process. Maybe you’ll use other tools to help you create your business strategy, such as the Strategy Diamond or SWOT analysis.
One important thing to do is to decide which factors you will track on an ongoing basis. You should not just track the data but agree when it will be reviewed again.
PEST Pitfalls to Avoid
Some common pitfalls to avoid when conducting your PEST Analysis include:
- Making assumptions rather than collecting hard facts.
- Trying to collect too much data. There is an almost infinite number of factors you could collect and it’s very easy to try and collect too much. The real key to a successful PEST Analysis is limiting the data you’ll collect to a small set of factors.
- Conducting your PEST Analysis and then forgetting about it. Factors that are important to your business should be tracked and monitored over time.
- Thinking that a PEST Analysis is all you need to do to formulate your strategy for a market. It isn’t. As already stated a PEST Analysis is just one input to strategy creation.
PEST Analysis Example
In this example, we’ll create a PEST Analysis for a company that is considering launching its electric car in the United Kingdom.
In this hypothetical example our PEST Analysis might look something like this:
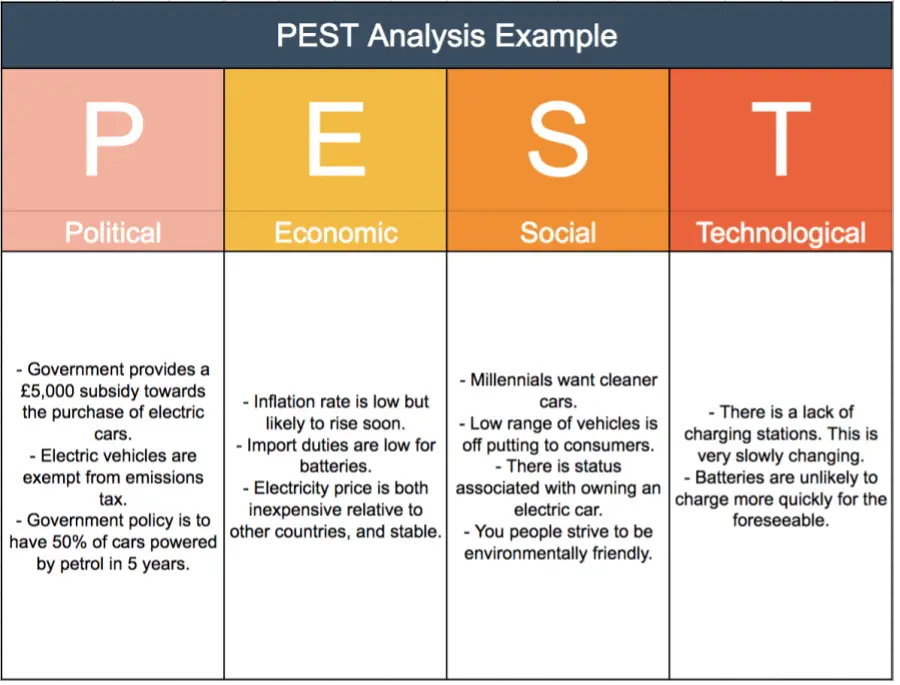
As you can see from the image, we’ve collected many macroeconomic factors that could potentially have a huge impact on our electric car business, including:
- Government policies are very favorable.
- The local population strives to be environmentally friendly. This is especially true for young people.
- The low range of electric cars is offputting for consumers.
PEST Analysis Template
If you’d like to download the PEST Analysis that we used in the above example you can find it here.
Variations on PEST Analysis
There are many variations on PEST Analysis. These variations exist to highlight additional specific factors. The most common of these variations are:
- PESTEL/PESTLE: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors.
- SLEPT: Social, Legal, Economic, Political, and Technological factors.
- STEPE: Social, Technological, Ecological, Political, and Economic factors.
- STEEPLED: Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, Ethical, and Demographic factors.
- DESTEP: Demographic, Economic, Social, Technological, Ecological, and Political factors.
- SPELIT: Social, Political, Economic, Legal, Intercultural, and Technological factors.
This looks like a complex list of variations but in practice its pretty simple. All you need to do is use one of these instead of the classic PEST Analysis if one of them looks more appropriate to your organization.
Summary
A PEST Analysis involves scanning different macroeconomic factors to understand long-term trends. From this, you can understand how these trends might impact on your business.
A PEST Analysis helps you avoid macroeconomic data overload and decide what factors are most important to your business.
This data can then be used to help you take advantage of opportunities locally, whilst avoiding threats. The basic idea is that by better understanding what’s happening in the world around you’ll be able to make better decisions.