Price comparison sites allow users to compare the prices of different products within a particular domain, for example, home and car insurance.
Let’s examine the price comparison website business model in terms of the Business Model Canvas introduced in a previous article, by going through each of the 9 building blocks in turn. To keep things simple we’ll stick to consumer focussed companies rather than business to business companies.
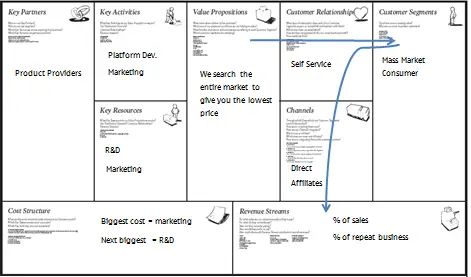
1. Customer Segments
Most of these types of business will target the mass market consumer segment, but smaller companies may target niches of consumers, for example, the owners of performance cars or the owners of expensive homes.
2. Value Proposition
The value proposition is based on offering a low price. This type of business is saying that by comparing all of the companies in the market we can get you the best insurance deals, parcel delivery/courier deals, and even broadband deals.
3. Channels
There are typically two channels that this business model will use. Direct to consumer via the Internet is one, and via affiliates is the other. The affiliates will then advertise the comparion site on their website and take a cut of any products sold.
4. Customer Relationships
The relationship with the customer is initially self-service, in that the customer does all the work to obtain a quote themselves. Often telephone and email backup is provided if there is a problem, or to help the customer make their payment.
5. Revenue Streams
The revenue streams are based on selling the products of others, the comparison site does not have any products of its own. Revenue is typically a percentage of each product sold.
6. Key Resources
The key resource in this type of business is the platform itself. The platform will either take batch feeds or communicate in real-time with each of the product providers. It must also provide a uncomplex user experience and journey to the customer.
7. Key Activities
The key activities of this type of business are twofold. They must be focussed on marketing, both to customers and to affiliates to drive eyeballs to the site. They will also be focussed on platform development, constantly improving the platform in a number of ways, including adding new products and making changes to increase the conversion rate.
8. Key Partnerships
The key partnerships will be with those businesses with whom the platform must integrate in order to sell their products.
9. Cost Structure
The majority of costs incurred in this type of business come from marketing activities. The next biggest cost will be the human resources needed to maintain and develop the platform. For an insurance comparison business the cost structure will be very different to traditional insurers, as an insurance comparison business is not an insurance business but a platform business using marketing to attract consumers.
Summary
The above descriptions should make the price comparison site business model easy to understand at a high level. Below you will see this information sketched on to the business model canvas we looked at previously:
If you were interested in developing this model further or disrupting the market then a next step might be to get people together from diverse backgrounds and examine ideas around what could be changed in each box of the business model canvas to gain a competitive edge.