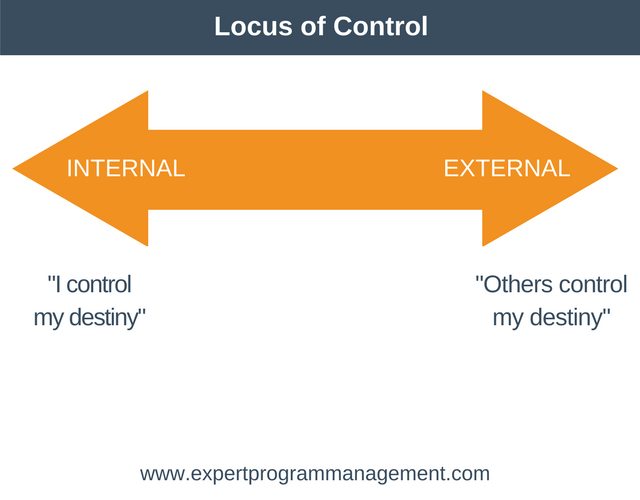
Locus of control relates to how much a person believes they have control over events in their life. A person with an internal locus of control believes they can influence events in their lives. A person with an external locus of control believes their life is controlled by external factors that they cannot influence.
Those with an internal locus of control believe events in their life are the result of their actions. Those with an external locus of control blame external factors for events in their lives.
As an example, consider students who fail an exam. A student with an internal locus of control might conclude that they didn’t work hard enough. A student with an external locus of control might conclude that their teacher has let them down.
Background
Julian Rotter developed the locus of control model in 1966. Rotter was an American psychologist. He developed the model whilst working at the University of Wisconsin.
It surprised Rotter how much attention the model received. He claimed that it was like lighting a cigarette and starting a forest fire!
Advantages and Disadvantages
In a very general sense, it is considered healthier to have an internal locus of control. However, there are advantages and disadvantages to each.
Internal Locus of Control Advantages
These people tend to be more successful in the workplace and they tend to:
- Take responsibility for events that happen to them, both good and bad.
- Work hard to get what they want.
- Be less influenced by the opinions of others.
- Take action to improve their situation.
- Learn from their mistakes.
- Be more successful.
Internal Locus of Control Disadvantages
There are also a few drawbacks associated with having an internal locus of control. They:
- Have a tendency to be direct and to the point. This can leave people feeling ‘trampled’.
- Can find it difficult to delegate, wanting to control everything.
External Locus of Control Advantages
There aren’t many advantages to having an external locus of control, but they include:
- Being a good team player.
- They can be good at “letting go” of stressful situations, and can thus be happier people.
External Locus of Control Disadvantages
The disadvantages associated with an external locus include are that they:
- Tend to blame external factors for events that happen to them.
- Often feel powerless or hopeless.
- Play down their success, attaching it to luck.
- Give up faster when obstacles present themselves.
- Feel like they are a victim.
Locus of Control Example in the Workplace
Suppose you gave a presentation at work. Afterwards, your boss tells you it was a poor presentation, lacking in clarity.
If you have an external locus of control you might blame the fact your brief was unclear. You might blame the fact that others weren’t forthcoming with the information you needed. You hope not to have the same problem again, provided these external factors don’t recur.
If you have an internal locus you would take responsibility for your poor performance. Yes, your brief was poor. Yes, you didn’t get all the information you needed. But you take responsibility for this and resolve to do better next time. You might do this by clarifying your brief upfront, and by chasing people for information earlier.
Optional Info: Attribution Theory
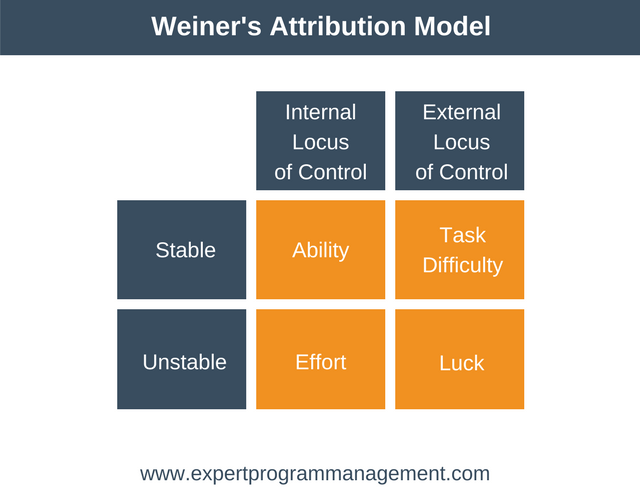
Attribution theory relates to how we attribute reasons to events that happen to us. The psychologist Bernard Weiner developed an attribution that applies to achievement. You can see the model in the diagram below:
As you can see, the columns are our locus of control. The rows are our stability. Stability, as defined in the model, refers to how likely your reasons are to recur. Suppose you failed an exam because bad traffic made you late. This would be an unstable attribution, as the event that caused you to fail would change next time you failed the exam.
Using this model, suppose a person with a high internal locus gave a great presentation. They would attribute it to their ability by saying something like, “I’m good at presentations”. They would expect the same success next time. Or they might attribute it to their effort by saying, “I worked hard”. This will give them encouragement to work hard next time.
Suppose a person with a high external locus gave a great presentation. They might attribute it to the task difficulty by saying, “It was easy”. If they gave a poor presentation they might alternatively attribute it to the difficulty of the task.
Locus of Control Quiz
To find out whether you have an internal or external locus of control you can take a quiz
here.
If you don’t like your results, then it’s sort of funny that the model predicts that you’ll blame others!
How to Develop an Internal Locus of Control
People with an internal locus believe they are in control of their destiny. Because of this they set goals and work hard to achieve them. They get creative or work harder when obstacles arise. Is it any wonder they are more successful in the workplace?
People with an external locus of control believe events happen to them. They don’t set goals because they believe what will be will be. This is also the reason they give up when challenges and obstacles arise.
If there is a key to developing an internal locus of control it’s this. Understand that both types are self-fulfilling. If you think your fate is in the hands of others you act to confirm that belief. If you think that your fate is under your control you will act to confirm that belief.
Thus, each of the tips below has a point. Namely, to get you to begin the slow process of realizing that you do have some control over your fate. The good news is that even small progress can have a big benefit once the self-fulfilling aspects start to kick in.
1. Set goals
Learn how to set goals for yourself. Start small. Identify one or two things you can achieve in the next few weeks.
You can learn more about goal setting
here.
2. Develop Your Problem Solving Skills
By developing your problem-solving skills you’ll become more confident. Instead of saying, “why me?” when problems arise you’ll be able to coolly analyze the alternatives and select the right option for you.
3. Watch Out for Self-Talk
Watch out for when you hear yourself saying things to yourself like, “I can’t do it!” or “There’s no point!”. If you don’t catch these thoughts then very soon you’ll start to believe what you’re saying to yourself.
Take a step back and remind yourself that you do have some choice, and you can make some difference.
Whether you think you can, or you think you can’t. You’re right.
Henry Ford
To learn more about catching self-talk and choosing empowering beliefs, read
this article.
Summary
Locus of control refers to the extent to which someone believes their fate is the result of their actions. Someone with an internal locus believes their fate is the result of their actions. Whereas someone with an external locus believes external events determine their fate.